[Ensemble] Gradient Boosting
1. Gradient Boosting
-
AdaBoost는 오분류 관찰치에 가중치를 올리는 방법
([Ensemble] Intro to Boosting & AdaBoost - Data Science (whatsdata.github.io)
-
이에 반해, Gradient Boosting은 직전 단계의 오차를 학습하는 방법임.
1.1. Idea
-
$Y = h_1 (x) + e_1$
-
$e_1 = h_2(x) + e_2$
-
$e_2 = h_3(x) + e_3$
-
$Y = h_1(x) + h_2(x) + h_3(x) + e_3$
$\vdots$
-
$\hat{Y} = w_1 h_1(x) + w_2 h_2(x) + w_3 h_3(x) + \cdots + w_m h_m (x)$
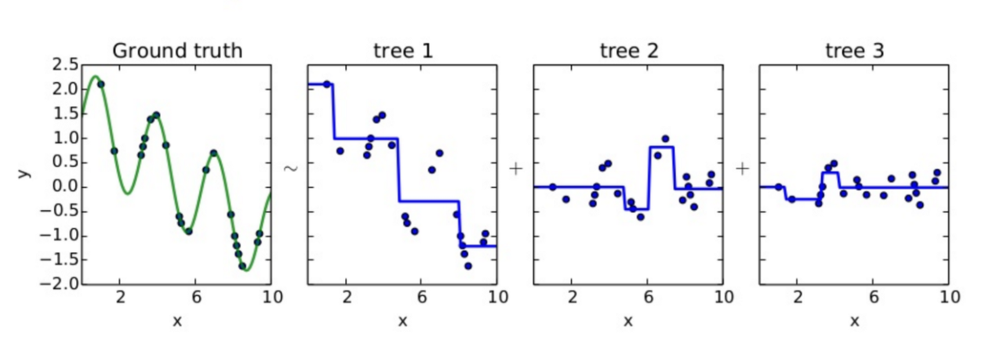
- tree를 base learner로 사용한다고 쳤을 때, tree 1을 통해 예측하고 남은 잔차를 tree2로 예측하고, 2의 잔차를 3으로 예측하고.. 하면서 이를 결합한 강한 분류기 (Strong learner)를 만들어갑니다.
#
1.2. Why Gradient?
-
Gradient Boosting이라고 칭하는 이유는, Loss function이 Squared error라면 negative gradient = Residual이 성립하기 때문.
-
Loss가 다음과 같을 때, \(L(f) = \sum_{i=1}^n L(y_i ,f(x_i))\)
-
gradient를 구하면 다음과 같다.
-
즉, Graident가 residual의 음수이기 때문에 residual을 이용한다. 만일, Loss function이 달라진다면 더이상 residual을 사용하지 않고 다른 함수를 사용할 수도 있다.
-
예시) Classification $(y_i \in {0,1})$
1.3. Algorithm
wikipedia 참고
1. Initialise model with a constant value
- $F_0 (x) = arg \underset{\gamma}{min} \sum_{i=1}^n L(y_i ,\gamma) $
2. For m=1 to M :
-
Compute so-called $pseudo - residual $ (which is residual for regression case) \(r_{im} = \nabla L(F_m) = {\large \frac{\partial L(y_i , F(x_i)_m)}{\partial F(x_i)_m)} }, \quad i = 1, \cdots ,n\)
-
Fir a base learner (or a weak learner, like tree) closed under scaling $h_m (x)$ to pseudo-residuals
-
compute multipler $\gamma _m$ by solving the following one-dimensional optimization problem
\(\gamma_m = \underset{\gamma}{arg min} \sum_{i=1}^n L(y_i , F(x_i)_{m-1} + \gamma h_m (x_i))\) -
Update the model \(F_m (x) = F_{m-1} (x) + \gamma_m h_m (x)\)
3. Output $F_M (x)$
2. GB code from scratch
- train_X, train_y, test_X, test_y를 구축하여 test error를 구하는게 목적
- Initial model로는 Decision Tree Classifier를 사용하고, 이후로 훈련할 때는 Decision Tree Regressor 이용
- 101번 반복하며, 1과 0으로 나누는 Classification 학습.
- Learning rate는 임의로 0.1에 고정시킴.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import os
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier, DecisionTreeRegressor
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn import metrics
digits = load_digits()
train_size = 1500
train_x, train_y = digits.data[:train_size], digits.target[:train_size]
test_x, test_y = digits.data[train_size:], digits.target[train_size:]
def GradientBoost(n_estimators, learning_rate, cutoff):
# The first classifier(C_0)
first_classifier = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3, random_state=0)
# Fit
first_classifier.fit(train_X, train_y)
# Predict with probability
# from the example of classification above, we use y_i - p_i as a residual
train_pred = np.array(first_classifier.predict_proba(train_X)[:,1])
test_pred = np.array(first_classifier.predict_proba(test_X)[:,1])
# Residual
resid = (train_y - train_pred)
# Regressor tree (for B = 100)
for b in range(1, n_estimators+1):
regressor_tree = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=3, random_state = 0)
# Fit
regressor_tree.fit(train_X, resid)
# Predict
reg_train_pred = regressor_tree.predict(train_X)
reg_test_pred = regressor_tree.predict(test_X)
# Update prediction using Gradient Descent Method
train_pred = train_pred + learning_rate * reg_train_pred
test_pred = test_pred + learning_rate * reg_test_pred
# Update Residual
resid = (train_y - train_pred)
# Lastly, if prediction result is over cutoff, return 1, else return 0
train_pred_result = np.array([1 if prob > cutoff else 0 for prob in train_pred])
test_pred_result = np.array([1 if prob > cutoff else 0 for prob in test_pred])
return test_y, train_pred_result, test_pred_result
GB code from sklearn
1. Load data & packages
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn import metrics
import numpy as np
digits = load_digits()
train_size = 1500
train_x, train_y = digits.data[:train_size], digits.target[:train_size]
test_x, test_y = digits.data[train_size:], digits.target[train_size:]
np.random.seed(123456)
2. Create ensemble
# Create the ensemble
ensemble_size = 200
learning_rate = 0.1
ensemble = GradientBoostingClassifier(max_depth = 3,
n_estimators = ensemble_size,
learning_rate = learning_rate)
ensemble.fit(train_x, train_y)
3. Print result
# Evaluation
gradient_digit_predictions = ensemble.predict(test_x)
gradient_digit_acc = metrics.accuracy_score(test_y, gradient_digit_predictions)
print("Gradient Boosting")
print("Accuracy: %.2f" % gradient_digit_acc)
Gradient Boosting
Accuracy: 0.88
Leave a comment